When we think about indoor comfort, one of the most important systems that often gets overlooked is the HVAC system. HVAC, which stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, is the backbone of climate control in homes, offices, and other buildings. However, how is HVAC control managed? Understanding this is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their system, reduce energy consumption, and maintain an ideal indoor environment.

HVAC control refers to the systems and mechanisms that regulate the performance of heating, cooling, ventilation, and air quality within a building. These control systems ensure that your HVAC equipment is working efficiently and effectively to maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
Defining HVAC Control Systems
At its core, HVAC control involves monitoring and adjusting temperature, humidity, airflow, and air quality within a building. The goal is to provide a consistent and comfortable environment for occupants while also minimizing energy use.
Some of the most common HVAC systems include:
- Heating: Using furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps to warm a space.
- Cooling: Air conditioners or cooling units that lower the temperature.
- Ventilation: Ensuring the exchange of stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air.
- Air Filtration: Using filters to clean the air of dust, allergens, and pollutants.
How HVAC Control Works
At a basic level, HVAC control works by using a combination of sensors, controllers, and manual or automated devices to monitor and adjust the systems. Here’s a quick breakdown of the process:
- Sensors: These are devices placed around your home or building that detect temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and even air quality.
- Thermostats: Often the central component, thermostats control the temperature of your space by signaling the HVAC system to turn on or off based on your settings.
- Control Boards/Actuators: These are the “brains” of your HVAC system, processing data from sensors and making decisions on when and how the system should activate (e.g., starting the fan, activating the heater, or turning on the cooling system).
- Dampers and Valves: These components help regulate airflow by opening and closing certain ducts, directing heated or cooled air where it’s needed most.
As an example, imagine you have a smart thermostat controlling your home’s HVAC system. This thermostat will constantly monitor the temperature of your home, and when it detects that the room temperature has deviated from your pre-set comfort level, it will signal the system to heat or cool the space as needed. All of this happens automatically, ensuring minimal intervention from you, the homeowner.
The Role of HVAC Control in Comfort and Efficiency
Effective HVAC control has a direct impact on both comfort and energy efficiency:
- Comfort: By adjusting the temperature, humidity, and airflow to precise levels, HVAC control ensures that your home or building is always at the ideal comfort level.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper HVAC control helps to minimize energy waste by ensuring the system runs only when necessary. For example, smart thermostats can learn your schedule and adjust the temperature based on when you are home or away, reducing the need for the system to run when it’s not needed.
In essence, how HVAC control is managed plays a key role in determining both how comfortable your space feels and how much energy it consumes. Understanding this can help you make informed decisions about managing your system for optimal performance.
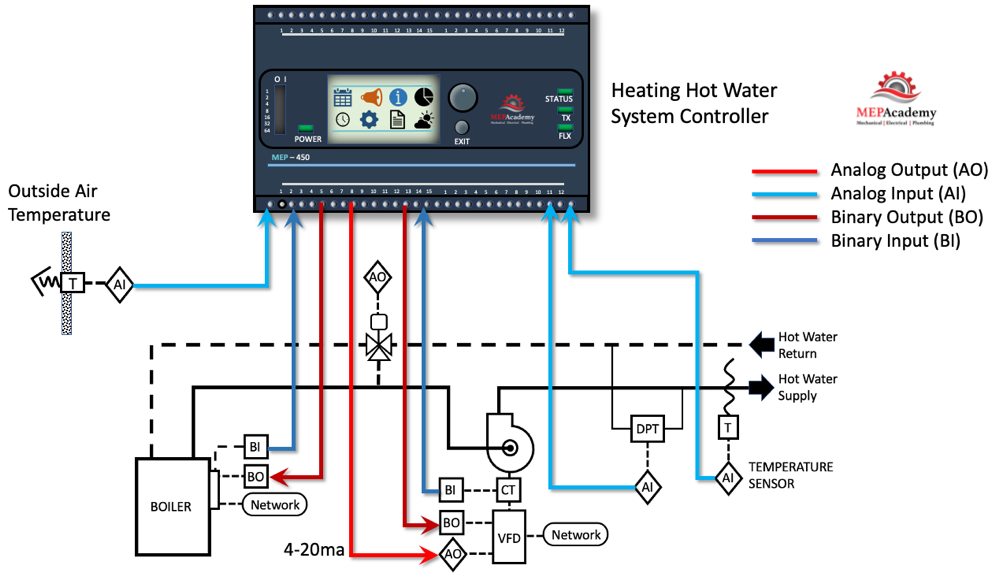
What Are the Types of HVAC Control Systems?
When it comes to HVAC control, understanding the different types of systems available can help you determine the best option for your needs, whether you’re managing a large commercial space or optimizing your home comfort. HVAC control systems vary in complexity, features, and automation. Let’s break down the types of HVAC control systems you might encounter and what makes each unique.
Manual vs. Automated HVAC Control
Manual HVAC Control Systems
In the past, most HVAC systems were controlled manually through basic thermostats or dials. These systems require you to set the temperature, and they will maintain it by turning the heating or cooling elements on or off. While simple and effective, manual HVAC control doesn’t allow for much flexibility or energy efficiency beyond basic temperature adjustments.
- Pros:
- Simple to use
- Reliable
- No need for Wi-Fi or app control
- Cons:
- Limited functionality
- Doesn’t adjust to changes in schedule or behavior
- Can waste energy by running unnecessarily
Automated HVAC Control Systems
Automated HVAC control systems have revolutionized the way we manage indoor environments. These systems use technology to optimize temperature, humidity, and air quality without the need for constant manual intervention. Automated systems often include features such as:
- Programmable Thermostats: Allow users to set specific temperatures for different times of the day or week.
- Smart Thermostats: These learn your habits and adjust settings automatically, even integrating with your phone or home automation system. Brands like Nest or Ecobee are popular examples.
- Zoning Systems: These systems divide a building into different zones, each with its own temperature control, allowing for customized comfort in each area.
Advantages of Automated HVAC Control:
- Enhanced Comfort: The system adjusts to your preferences, ensuring consistent comfort throughout the day.
- Energy Efficiency: By learning your routine and adjusting accordingly, automated systems prevent heating or cooling an empty house, saving you money on utility bills.
- Remote Access: Many smart thermostats can be controlled from your smartphone, enabling you to adjust settings while away from home.
Centralized vs. Decentralized HVAC Control
Centralized HVAC Control
In larger buildings—like office complexes, schools, or hospitals—a centralized HVAC control system is typically used. This means there is one control system that manages the heating, cooling, and ventilation for the entire building. Centralized systems are ideal for large-scale environments because they offer easier maintenance and centralized monitoring.
How centralized HVAC control works:
- Central Control Units: A single control unit that communicates with various sensors and actuators throughout the building.
- Ductwork and Vents: Air is distributed through a network of ducts to different rooms or zones.
- Energy Management: Centralized systems can be equipped with energy management software to help monitor and optimize usage.
Advantages of Centralized HVAC Control:
- Efficiency: It’s easier to maintain a uniform temperature and air quality across a large area.
- Cost-Effective: For large buildings, a centralized system is often more cost-effective in terms of installation and maintenance than installing separate systems for each room.
- Real-time Monitoring: Centralized control allows building managers to monitor performance and energy use from one location.
Decentralized HVAC Control
In smaller buildings or homes, decentralized HVAC control is common. Each unit operates independently, meaning there is no central control that governs the entire building. For example, an apartment might have a separate HVAC system in each room, each with its own thermostat.
Advantages of Decentralized HVAC Control:
- Personalized Comfort: You can adjust the temperature in individual rooms to your liking, which is perfect for homes with multiple occupants.
- Flexibility: You can control the system room by room, which is more efficient if you’re only using certain areas of the house at different times of day.
- Installation Flexibility: Easier to install and doesn’t require extensive ductwork, which can be an advantage in retrofitting buildings.
However, decentralized systems can sometimes be less efficient in terms of energy use, especially if you’re heating or cooling unoccupied rooms.
Smart HVAC Control Systems: The Future of Temperature Regulation
As technology continues to advance, smart HVAC control systems are becoming more common in residential and commercial buildings. These systems are connected to the internet and can be controlled remotely via smartphones, voice assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, and other smart home devices. The integration of smart technologies helps to make HVAC systems more adaptive, intuitive, and efficient.
Features of Smart HVAC Control Systems:
- Learning Algorithms: Smart thermostats learn your schedule and preferences, adjusting the temperature automatically.
- Remote Access: Control your HVAC system from anywhere using your phone or tablet.
- Energy Usage Insights: Many smart systems offer detailed reports on energy consumption, so you can track how much you’re saving.
- Geofencing: Some systems use your phone’s location to determine when you’re on your way home and adjust the temperature accordingly.
Benefits of Smart HVAC Control:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: The system optimizes your heating and cooling patterns based on when you’re home and active, reducing energy waste.
- Convenience: The ability to adjust the system remotely means you can control your environment from anywhere, making it especially useful for those with busy schedules.
- Increased Comfort: Smart HVAC systems can adapt to changes in external weather or internal preferences, offering a more personalized indoor climate.
Zoning and Multi-Zone HVAC Systems
One of the most advanced ways to manage HVAC control is through zoning. Zoning divides a building into different areas or “zones,” each with its own thermostat. This allows for more precise control over temperature and airflow in various rooms.
How Zoning Works:
- Dampers: Automated dampers installed in the ductwork control the flow of air to different zones based on the settings of the thermostat in each zone.
- Separate Thermostats: Each zone has its own thermostat, so different areas of the building can be heated or cooled independently.
Advantages of Zoning:
- Energy Savings: Instead of heating or cooling the entire building, you can direct the energy where it’s needed most.
- Comfort Control: If some areas of the building are used more frequently than others, you can adjust the temperature accordingly, without affecting unused spaces.
- Flexibility: Zoning systems allow for temperature control based on the specific needs of each room or area.
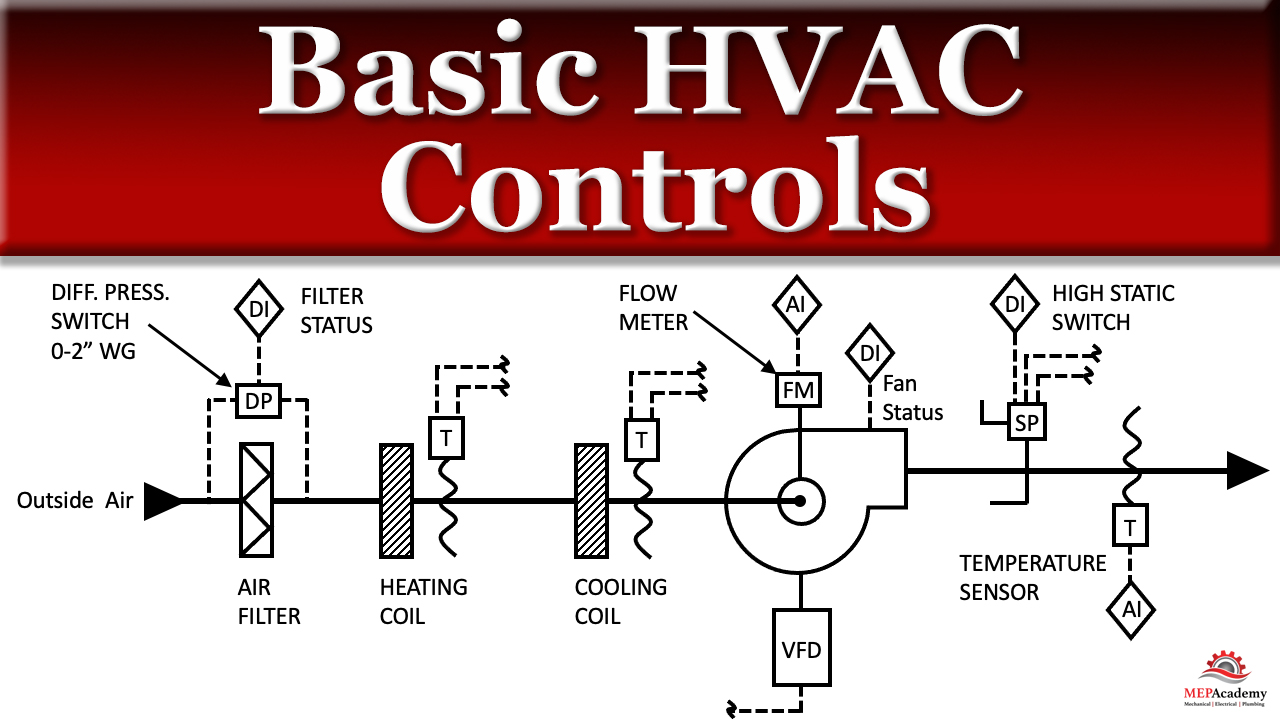
Factors That Influence HVAC Control
Understanding the key factors that influence HVAC control is essential for optimizing your system. These factors dictate how effectively your system regulates the environment, from temperature to air quality, and can significantly affect energy consumption. Let’s explore the primary elements that HVAC systems manage and how they impact both comfort and efficiency.
Temperature Control: Maintaining the Ideal Climate
One of the most fundamental aspects of HVAC control is temperature regulation. Whether you are heating or cooling a space, ensuring the correct temperature is maintained is crucial for both comfort and energy efficiency.
How HVAC Systems Control Temperature:
- Thermostats: These devices serve as the control centers for temperature. When you set your thermostat to a specific temperature, the system will adjust its heating or cooling mechanisms to maintain that level. For instance, if your thermostat is set to 72°F, the system will activate the heater if the temperature drops below this point or the AC if it rises above it.
- Sensors: Many modern HVAC systems include temperature sensors that monitor the environment continuously. These sensors detect any fluctuations and send feedback to the control unit, which adjusts the system’s operation accordingly. The more sensors you have, the more precise the temperature regulation.
Importance of Temperature Control:
- Comfort: Proper temperature control ensures that your living or working space remains comfortable year-round. Whether it’s keeping the chill off during winter or cooling down in the summer, HVAC systems play a critical role.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper calibration of your thermostat can save a significant amount of energy. For example, setting your thermostat to 78°F during summer and 68°F during winter is optimal for energy savings.
Best Practices for Temperature Control:
- Avoid setting the thermostat to extreme temperatures. It may seem tempting to turn the AC to 60°F in the summer or the heater to 80°F in the winter, but these temperature extremes can cause the system to overwork, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Regular calibration of thermostats is essential to ensure that the readings are accurate and the system is not overcompensating.
Humidity Control: Balancing Comfort and Health
Another vital aspect of HVAC control is regulating humidity. Humidity plays a significant role in how comfortable an indoor space feels. High humidity can make the air feel warmer than it is, while low humidity can cause discomfort and even health issues like dry skin and respiratory problems.
How HVAC Systems Control Humidity:
- Dehumidification: Many modern HVAC systems are equipped with dehumidifiers or have the ability to reduce humidity as part of the cooling process. Air conditioners, for instance, naturally remove moisture from the air while cooling.
- Humidifiers: In some systems, a humidifier may be incorporated, especially in dryer climates, to add moisture to the air. This is essential for maintaining comfort and preventing health issues like dry eyes, throat irritation, and static electricity.
Importance of Humidity Control:
- Health Benefits: Proper humidity control can prevent the growth of mold and mildew, which thrive in overly humid environments. It can also help prevent respiratory issues that arise from dry air.
- Comfort: Maintaining the right humidity level can make the air feel more comfortable. For instance, during summer, humidity levels above 60% can make the heat feel even more oppressive, while winter air tends to be too dry, making it feel colder than it actually is.
Best Practices for Humidity Control:
- Use a humidity monitor to track levels in different rooms and adjust accordingly.
- If your HVAC system does not include built-in humidifiers or dehumidifiers, consider adding them as an extra feature to improve comfort and air quality.
Air Quality and Ventilation: A Key Component of HVAC Control
Good air quality is an often-overlooked benefit of HVAC control. Not only does it affect the comfort level of a space, but it can also impact the health of everyone inside. The air in many homes and offices can contain allergens, dust, pollutants, and pathogens. HVAC systems play a crucial role in improving air quality through proper ventilation and filtration.
How HVAC Systems Improve Air Quality:
- Air Filtration: Modern HVAC systems use high-efficiency filters to trap particles like dust, pollen, and pet dander. Filters come in different grades, with HEPA filters being the most effective at removing airborne particles.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation helps to bring in fresh air and expel stale indoor air. Many HVAC systems use an air exchange unit that pulls in outdoor air and removes indoor air. In homes or buildings with poor ventilation, air exchangers or HRVs (Heat Recovery Ventilators) help to improve airflow and reduce CO2 levels indoors.
Importance of Air Quality Control:
- Health and Comfort: Clean air reduces the risk of allergies, asthma, and respiratory infections. Proper ventilation can help minimize CO2 buildup, ensuring that you breathe fresh, oxygen-rich air.
- Energy Efficiency: A well-maintained air filtration system can ensure that your HVAC system operates efficiently. Dirty filters restrict airflow, causing the system to overwork and use more energy.
Best Practices for Air Quality Control:
- Change filters regularly (typically every 1-3 months, depending on usage and filter type).
- Ensure that air vents are not blocked by furniture or curtains to maintain optimal airflow.
- Consider installing air purifiers if you live in an area with high levels of pollutants or if anyone in your household suffers from allergies.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Control: Maximizing Savings
Perhaps one of the most compelling reasons for managing HVAC control is the potential to save on energy costs. HVAC systems are among the biggest energy consumers in a building, but effective HVAC control can help significantly lower utility bills.
How HVAC Control Impacts Energy Efficiency:
- Programmable Thermostats: Setting your HVAC system to run only when needed, such as adjusting the temperature before you arrive home or before bedtime, ensures that you don’t waste energy when it’s not necessary.
- Smart Thermostats: These systems adapt to your lifestyle, learning when you’re typically home and adjusting accordingly. Many smart thermostats also have features that suggest energy-saving settings based on your usage patterns.
Importance of Energy Efficiency:
- Lower Utility Bills: By fine-tuning your HVAC system to only run when needed, you avoid the costly mistake of heating or cooling an empty building.
- Environmental Impact: Reducing energy consumption directly lowers your carbon footprint, making your building more sustainable and eco-friendly.
Best Practices for Energy Efficiency:
- Set your thermostat to the right temperature (78°F in summer and 68°F in winter are ideal for energy savings).
- Consider installing insulation or upgrading windows to ensure your HVAC system doesn’t have to work harder than necessary.
- Use ceiling fans to help circulate air, allowing you to set your thermostat a few degrees higher in summer without sacrificing comfort.
How to Set Up HVAC Control Systems for Maximum Efficiency
Now that we have covered the key factors influencing HVAC control, it’s time to delve into how you can set up HVAC control systems for maximum efficiency. Whether you’re installing a new system or optimizing an existing one, the right setup can drastically improve comfort levels and reduce energy consumption.
1. Proper Installation of Thermostats and Sensors
The first step in ensuring efficient HVAC control is the correct installation of thermostats and sensors. The placement and calibration of these components directly impact the accuracy and responsiveness of your HVAC system.
Tips for Installing Thermostats:
- Location: Thermostats should be installed in an area that reflects the average temperature of your home or building. Avoid placing them near windows, doors, or heat-producing appliances like lamps and televisions, as they can cause inaccurate readings.
- Height: Install the thermostat at an average height (about 5 feet from the floor) so it can effectively measure the room’s temperature. This is especially important for homes with high ceilings or open-concept areas.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Ensure your thermostat is not exposed to direct sunlight, as this can skew its readings and lead to inefficient temperature control.
Sensor Placement:
- Sensors help regulate temperature and air quality more effectively. These should be installed in key areas, such as living rooms, bedrooms, and hallways.
- For optimal control, consider using multiple sensors throughout the building, especially if you’re working with a zoning system.
2. Programmable and Smart Thermostat Settings
Once your thermostat and sensors are properly installed, it’s important to make sure they are configured correctly for maximum efficiency. Programmable thermostats and smart thermostats are great tools for this, allowing you to automate temperature adjustments based on your schedule and preferences.
How to Program Your Thermostat:
- Create a schedule: Set your thermostat to automatically adjust the temperature based on your typical routine. For example, program it to lower the temperature during the night or when you’re away from home, and increase it before you wake up or return from work.
- Seasonal Adjustments: In summer, set the thermostat to 78°F while you’re home and raise it to 85°F when you’re away. In winter, set it to 68°F while you’re home and lower it to 60-62°F when you’re away.
- Override feature: If you need to make quick adjustments, most programmable thermostats offer an override feature to change settings temporarily without affecting the schedule.
Benefits of Smart Thermostats:
- Learning Capabilities: Smart thermostats like the Nest or Ecobee learn your behavior over time, automatically adjusting to your preferences.
- Remote Control: Many smart thermostats allow you to control the system from your smartphone, so you can adjust the temperature while away from home.
- Energy Reports: Smart systems provide detailed reports on your energy consumption, helping you track how much energy you’re using and find areas where you can reduce waste.
3. Maintaining HVAC Systems for Optimal Control
Proper maintenance is one of the most important factors in ensuring that your HVAC system operates efficiently. Regular care not only helps extend the lifespan of your system but also ensures that it runs smoothly and doesn’t consume unnecessary energy.
Key Maintenance Tasks:
- Filter Changes: Change the filters in your HVAC system regularly. Clogged filters restrict airflow, making the system work harder and reducing its efficiency. Depending on the type of filter and usage, this should be done every 1-3 months.
- Cleaning Coils and Ducts: Clean the evaporator and condenser coils at least once a year to ensure they are not obstructed by dirt or debris. Similarly, clean the ductwork to remove dust and other particles that can reduce airflow and decrease efficiency.
- Check Refrigerant Levels: If your air conditioner is low on refrigerant, it can lead to poor cooling performance. Having a professional check and top up the refrigerant can help maintain efficiency.
- Inspect Insulation: Ensure that ducts, pipes, and the attic are properly insulated. Leaky ducts or poorly insulated areas can cause energy loss, making your HVAC system less effective.
Schedule Professional Maintenance:
- Even with regular DIY maintenance, it’s important to have your HVAC system inspected by a professional at least once a year. A technician can identify potential issues before they become expensive repairs and ensure that all components are functioning optimally.
4. Balancing Comfort and Efficiency
Achieving the perfect balance between comfort and energy efficiency is a delicate task. While it’s tempting to set your thermostat to extreme temperatures during very hot or cold weather, this can cause your system to overwork and significantly increase your energy bills. Here are some tips to balance both:
Set Moderate Temperatures:
- Summer: Instead of cranking the AC to the lowest setting, aim for 78°F during the day and 82°F at night. Use ceiling fans to help circulate the air and maintain comfort at slightly higher temperatures.
- Winter: During the colder months, set your thermostat to 68°F when you’re home and lower it by 5-10°F at night or when you’re away.
Use Ceiling Fans:
- Ceiling fans help circulate air and make the room feel cooler in summer or warmer in winter. In the winter, set the fan to rotate clockwise at a low speed to circulate warm air that rises to the ceiling, while in the summer, set it to rotate counterclockwise to create a cooling breeze.
Close Doors and Vents in Unused Rooms:
- If you’re not using certain rooms, close off the vents and doors to limit airflow to these spaces, allowing your system to focus energy on rooms that are in use.
5. Upgrading to Energy-Efficient HVAC Equipment
In some cases, the best way to improve HVAC control efficiency is by upgrading the equipment itself. Older HVAC systems are often much less efficient than newer models, which can lead to higher energy consumption and repair costs. Here are some upgrades to consider:
Energy-Efficient Units:
- High-Efficiency Furnaces and AC Units: Look for units with a SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) of 14 or higher for air conditioners and an AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) of 90% or more for furnaces.
- Variable-Speed Motors: These motors can adjust the speed of the fan depending on the heating or cooling demand, helping to maintain more consistent temperatures while using less energy.
- Heat Pumps: Heat pumps are an efficient way to both heat and cool your home. They work by transferring heat instead of generating it, reducing the need for fossil fuels and lowering energy use.
Smart Controls and Automation:
- Consider integrating your HVAC system with a home automation system for more precise control. Devices like smart thermostats, zoning systems, and even voice-activated controls can provide even greater efficiency and comfort.