Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems play a crucial role in maintaining comfort, air quality, and energy efficiency in modern homes and businesses. But what exactly is HVAC, and why is it so important?
Before diving into the purpose of HVAC systems, it’s essential to understand what the acronym stands for and the role each component plays. HVAC refers to three primary functions:
- Heating: The process of raising the temperature of indoor spaces, ensuring comfort during cold weather.
- Ventilation: The movement of air throughout a space, which is vital for maintaining indoor air quality (IAQ) and controlling humidity levels.
- Air Conditioning: The cooling of indoor spaces to maintain comfort during hot weather.
Together, these systems work in tandem to create a balanced, controlled indoor environment. Let’s look at each component in more detail.
How HVAC Systems Have Evolved
The evolution of HVAC systems has come a long way since their inception. Early heating methods, such as stoves and fireplaces, were replaced by more efficient technologies like central heating and cooling systems. As homes and buildings grew larger and more complex, so did the need for more sophisticated HVAC systems that could handle both heating and cooling simultaneously.
Key milestones in HVAC development include:
- Early 1900s: The first air conditioning systems were developed, mainly for industrial use.
- 1920s: Central heating systems began to replace traditional heating methods.
- 1980s-2000s: The rise of energy-efficient models, programmable thermostats, and environmental consciousness led to smarter HVAC systems.
- Today: The introduction of smart HVAC systems that can be controlled remotely via apps, improved energy-saving features, and a greater emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly refrigerants.
With these advancements, HVAC systems have not only become more efficient but also much more affordable to operate.
Why Is HVAC Important? Understanding Its Purpose in Modern Homes and Businesses
So, why is HVAC so important? The purpose of HVAC systems extends far beyond simply keeping your home or office comfortable. Let’s take a deeper look at the many benefits HVAC systems provide.
Comfort and Well-being
One of the primary purposes of HVAC is to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Whether it’s the dead of winter or the peak of summer, HVAC systems regulate temperature and humidity to keep indoor spaces at a livable level.
- Heating ensures warmth during cold weather, which is essential for health and safety.
- Air conditioning helps to cool indoor spaces during hot weather, preventing discomfort, heat exhaustion, and other heat-related illnesses.
- Ventilation helps in controlling humidity, preventing mold growth, and promoting healthy airflow.
In a well-functioning HVAC system, all these elements work together to create a comfortable, balanced living or working space.
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Modern HVAC systems are designed with energy efficiency in mind, providing a great return on investment. By maintaining the optimal temperature and reducing unnecessary energy use, you can see a significant reduction in energy costs. In fact, heating and cooling typically make up more than half of a household’s energy bill.
- Energy-efficient systems can lower energy consumption by using smart thermostats, programmable schedules, and high-efficiency compressors.
- Upgrading to modern HVAC can save you up to 30% annually on energy costs.
- Proper insulation and sealing air ducts help to ensure that the heated or cooled air stays inside your home or business.
Choosing the right HVAC system for your space and regularly maintaining it can lead to substantial savings in the long run.
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
Another critical purpose of HVAC systems is maintaining indoor air quality (IAQ). Indoor air can often be more polluted than outdoor air due to trapped dust, allergens, pet dander, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from cleaning supplies or furniture. HVAC systems help improve IAQ by:
- Air filtration: Using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove allergens and pollutants.
- Ventilation: Bringing in fresh outdoor air and removing stale air.
- Humidity control: Preventing excess moisture that can lead to mold growth and reduce indoor air quality.
A clean HVAC system is key to a healthier indoor environment, especially for people suffering from respiratory conditions like asthma or allergies.
How Does an HVAC System Work? The Purpose and Function of Each Component
Now that we’ve covered why HVAC systems are important, let’s dive into the technical details. What is the purpose of HVAC components, and how do they work to create a comfortable and healthy indoor environment?
Heating
The heating component of an HVAC system is responsible for maintaining a warm indoor temperature during the colder months. Common heating methods include:
- Furnaces: These use gas, oil, or electricity to produce heat, which is then distributed through air ducts.
- Heat Pumps: These systems extract heat from the air outside (even in cold weather) and transfer it inside. They can also function as air conditioners in warmer months.
- Boilers: These use hot water or steam to heat your home, with the heat distributed through radiators or radiant floor systems.
The purpose of heating is to maintain a comfortable environment, ensuring that homes and businesses stay warm during colder seasons, while also preventing pipes from freezing or causing other weather-related damage.
Ventilation
Ventilation is the process of moving air through your home or building to maintain air quality and control moisture levels. There are two main types of ventilation in an HVAC system:
- Natural Ventilation: This is the passive flow of air through windows, vents, and cracks. While natural ventilation can work in some climates, it’s often not sufficient in more humid or polluted environments.
- Mechanical Ventilation: This involves powered fans, air ducts, and exhaust systems to circulate air more efficiently. It’s especially important in modern homes with airtight construction, where natural ventilation is insufficient.
The primary purposes of ventilation are to:
- Provide fresh air and remove stale indoor air.
- Control moisture to prevent mold growth and condensation.
- Maintain a comfortable humidity level, which can have a big impact on health and comfort.
Air Conditioning
The air conditioning component of HVAC systems is designed to cool the air and remove humidity during warmer months. The most common types of air conditioning include:
- Central Air Conditioners: These systems cool the air and distribute it through ducts to various rooms in the home or building.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: These are often used in smaller spaces or areas without existing ducts.
- Window or Portable Air Conditioners: These are more localized cooling systems used for individual rooms.
The purpose of air conditioning is to provide comfort in hot climates, prevent heat-related illnesses, and ensure that the indoor environment remains cool and pleasant, especially during extreme heat.
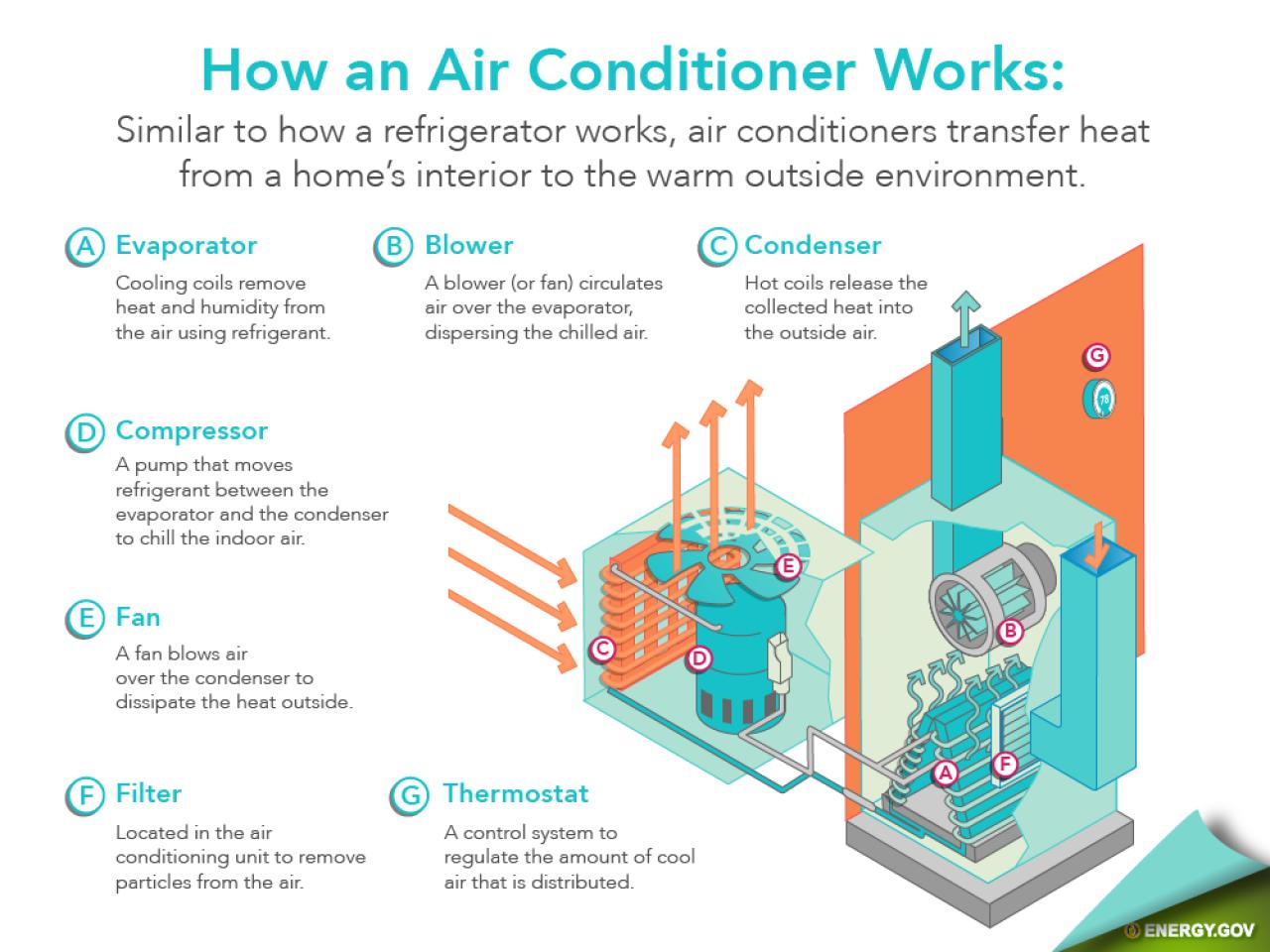
The Purpose of HVAC in Different Settings: Residential, Commercial, and Industrial Applications
While the purpose of HVAC systems is largely the same across all settings — to maintain a comfortable and healthy indoor environment — the way these systems are implemented and their specific roles can differ significantly depending on whether they’re used in a residential, commercial, or industrial setting. Let’s break down the unique needs of HVAC in each of these environments.
Residential HVAC Systems
In residential settings, HVAC systems are designed to provide optimal comfort and energy efficiency for families. Typically, these systems are scaled down compared to commercial or industrial systems but are still complex in their ability to regulate temperature, air quality, and humidity.
Common residential HVAC configurations include:
- Central Heating and Cooling Systems: These are the most common types of HVAC systems in homes. They use a furnace for heating and an air conditioner for cooling, with air circulated through ducts.
- Ductless Systems: Ideal for smaller homes or specific rooms, ductless mini-split systems are a popular choice for homes without pre-existing ductwork.
- Hybrid HVAC Systems: These systems combine a furnace and heat pump, allowing for energy-efficient heating and cooling based on the season.
The primary purpose of residential HVAC systems includes:
- Maintaining a consistent and comfortable temperature year-round.
- Enhancing indoor air quality through filtration, ventilation, and humidity control.
- Energy savings, particularly with the adoption of modern energy-efficient HVAC units, smart thermostats, and zoning systems.
Smart technology in residential HVAC has also revolutionized how homeowners control their comfort. Devices like smart thermostats (e.g., Nest, Ecobee) allow for remote control and energy-saving features, helping reduce costs while improving overall comfort.
Commercial HVAC Systems
Commercial HVAC systems are typically larger and more complex than residential ones because they must serve bigger spaces, accommodate more people, and provide services for varied applications (e.g., offices, stores, factories). The purpose of HVAC systems in commercial settings goes beyond just comfort—it includes meeting the specific demands of different business functions.
Key considerations in commercial HVAC systems include:
- Zoning: Commercial spaces often have multiple zones that need individualized temperature control. HVAC zoning systems use multiple thermostats and dampers to direct air to different areas based on their needs.
- Ventilation and Air Quality: Businesses that deal with large numbers of people (e.g., offices, gyms, restaurants) need HVAC systems to regulate air quality by circulating fresh air and filtering pollutants.
- Energy Efficiency: In commercial settings, HVAC systems must operate efficiently due to the large scale of the space and the amount of energy consumed. Variable refrigerant flow (VRF) and chilled beams are commonly used to improve energy efficiency.
The purpose of commercial HVAC systems is to:
- Ensure the comfort of employees, customers, and clients.
- Maintain air quality and ventilation to create a healthy, productive environment.
- Optimize energy use to reduce operating costs, especially in large buildings where climate control is needed for large spaces.
In fact, energy-efficient HVAC systems in commercial buildings can significantly lower utility bills, sometimes reducing costs by as much as 30%—a major concern for businesses looking to maximize profit.
Industrial HVAC Systems
Industrial HVAC systems are typically the most robust and specialized due to the harsh working conditions, large-scale facilities, and specific temperature control needs of industries such as manufacturing, warehousing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing.
These systems are not only responsible for controlling the environment in which workers operate but also for ensuring the safety and quality of products. The purpose of HVAC in industrial environments often extends to maintaining equipment efficiency, product integrity, and compliance with safety standards.
Key components of industrial HVAC systems:
- Exhaust Ventilation: Industrial HVAC systems often incorporate powerful exhaust fans and air filtration systems to remove fumes, smoke, dust, or toxic gases generated during manufacturing processes.
- Temperature Control: Many industrial settings, such as warehouses and manufacturing plants, need to regulate temperature to prevent equipment malfunctions or spoilage of materials. Some environments (e.g., food processing plants) may require precise temperature and humidity control to comply with health regulations.
- Air Distribution and Filtration: In manufacturing and pharmaceutical environments, HVAC systems need to filter out particulate matter or microorganisms, which could contaminate products or production lines.
The primary purpose of industrial HVAC systems is to:
- Regulate temperatures for both comfort and operational needs.
- Control ventilation to prevent the buildup of harmful chemicals, fumes, or dust.
- Protect sensitive equipment, materials, and products from the negative effects of temperature fluctuations or poor air quality.
For example, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, HVAC systems are crucial for ensuring cleanroom environments where specific temperature, humidity, and air purity levels must be strictly maintained.
What Are the Benefits of HVAC Systems? Exploring the Purpose Beyond Comfort
The purpose of HVAC systems goes far beyond just making a space comfortable. Modern HVAC technology brings a range of benefits that enhance both the quality of life and the value of a property. Let’s look at some of the other major benefits of HVAC systems:
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
One of the key benefits of modern HVAC systems is energy efficiency. As awareness of climate change grows and energy costs increase, HVAC manufacturers have made significant strides toward creating systems that use less energy while still providing effective climate control.
- High-efficiency furnaces and air conditioners use less fuel or electricity to deliver the same or better performance.
- Smart thermostats allow for more precise control over when and how much energy is used, ensuring that the HVAC system runs only when needed.
- Energy Star-rated HVAC units help homeowners and businesses reduce their carbon footprint and qualify for rebates or tax credits in some cases.
In fact, upgrading to an energy-efficient HVAC system can save homeowners and businesses up to 30% on energy bills annually, reducing overall operational costs.
Increased Property Value
Another purpose of HVAC systems is their potential to increase property value. A modern, well-maintained HVAC system can make your property more attractive to potential buyers, particularly in climates with extreme weather conditions.
- Homes or commercial properties with energy-efficient HVAC systems are highly sought after because they promise lower long-term costs for heating and cooling.
- Installing an HVAC system with advanced features like smart control, zoning, and improved air filtration can add significant value to your home or business.
- Many buyers view a newer HVAC system as a sign that the property has been well-maintained, making it more appealing and possibly yielding a higher sale price.
In fact, homes with newer HVAC systems tend to sell faster and for higher prices compared to those without.
Better Health Outcomes
While HVAC systems are primarily designed to improve comfort, they also play a crucial role in enhancing health outcomes. Properly functioning HVAC systems regulate humidity, improve air quality, and control temperature, all of which contribute to better health.
- Air filtration systems in modern HVACs help to remove allergens like dust, pollen, and pet dander, making it easier for individuals with asthma or allergies to breathe.
- Humidifiers and dehumidifiers integrated into HVAC systems maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing conditions like dry skin, mold, and mildew.
- In commercial and industrial settings, HVAC systems help to reduce the risk of airborne diseases by ensuring that air circulates and fresh air is continuously brought in.
By ensuring that indoor environments are free from pollutants and contaminants, HVAC systems support better respiratory health and overall well-being.
Enhanced Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
As indoor air can sometimes be more polluted than outdoor air, the IAQ benefits of HVAC systems cannot be overstated. The system’s ventilation and filtration capabilities play a critical role in maintaining a clean and healthy indoor environment.
- HEPA filters trap airborne particles and allergens, improving the overall quality of air.
- Air purifiers integrated into HVAC systems can help remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs), smoke, and other harmful gases.
- Constant air circulation prevents the buildup of stale air, ensuring the environment stays fresh and breathable.

Common HVAC Problems and How They Affect the Purpose of the System
While HVAC systems are designed to maintain comfort, air quality, and energy efficiency, they can sometimes face issues that disrupt their purpose and function. Recognizing and addressing common HVAC problems early on can prevent costly repairs and ensure your system operates efficiently.
Inefficient Heating or Cooling
One of the most common HVAC issues is inefficient heating or cooling, where the system fails to adequately warm or cool the space. This can be caused by a variety of factors:
- Dirty air filters: Air filters trap dust, debris, and other particles, but over time they can become clogged, reducing airflow and forcing the system to work harder. This leads to inefficiency and higher energy bills.
- Low refrigerant levels: In cooling systems, low refrigerant levels can result in poor cooling performance. This often occurs due to leaks in the system, and if not addressed, it can lead to compressor failure.
- Thermostat issues: If your thermostat is malfunctioning or improperly calibrated, it may not signal the HVAC system to maintain the desired temperature, causing inconsistencies in heating and cooling.
Impact on HVAC purpose: When an HVAC system is inefficient, it fails to maintain a comfortable indoor environment, forcing homeowners or businesses to use more energy to achieve the same results. This leads to higher utility costs, greater wear on the system, and decreased overall comfort.
Solutions: Regularly replace air filters, inspect refrigerant levels, and calibrate or replace faulty thermostats to keep your system running efficiently.
Poor Air Quality
An HVAC system is responsible for maintaining indoor air quality (IAQ) by filtering out pollutants and circulating clean air. However, if the system is not properly maintained, it can cause poor air quality.
Common causes of poor air quality include:
- Dirty or clogged air filters: Over time, filters accumulate dust and dirt, reducing their ability to trap allergens, bacteria, and pollutants.
- Leaky ducts: Leaky ducts can allow dust and debris to enter the air system, which then gets circulated throughout your home or business.
- Inadequate ventilation: If the HVAC system isn’t properly ventilating the space, stale air and harmful particles can accumulate indoors, leading to respiratory issues.
Impact on HVAC purpose: A malfunctioning HVAC system compromises the health benefits it provides by failing to properly filter or circulate clean air. Poor IAQ can trigger allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions.
Solutions: Regularly change filters, clean ducts, and consider installing air purifiers to improve air quality. Professional inspections can ensure the HVAC system is working to its full potential to protect your health.
Frequent Breakdowns
Frequent breakdowns can significantly affect the purpose of HVAC systems by disrupting comfort and causing major inconveniences. Some of the most common causes of frequent HVAC breakdowns include:
- Lack of regular maintenance: HVAC systems, like any complex machinery, require routine inspections, cleaning, and servicing. Neglecting regular maintenance can lead to issues like frozen coils, malfunctioning components, and overall system failure.
- Worn-out parts: Over time, components like compressors, motors, and fans wear out, causing the system to fail.
- Improper sizing: An HVAC system that is too large or too small for a space will experience additional strain, which can lead to breakdowns. A system that’s too large will cycle on and off frequently, while one that’s too small will run constantly and overheat.
Impact on HVAC purpose: Frequent breakdowns interfere with the primary function of HVAC systems—ensuring consistent temperature control, air circulation, and air quality. The result is discomfort, higher repair costs, and possibly a system replacement if issues aren’t addressed early enough.
Solutions: Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure all parts are functioning well, and consult with a professional for sizing and installation to avoid issues related to system capacity.
How to Maintain Your HVAC System to Ensure It Continues to Serve Its Purpose
Proper maintenance is key to keeping your HVAC system functioning as intended. Whether your goal is to maintain comfort, improve air quality, or enhance energy efficiency, regular maintenance ensures your system runs smoothly and reliably.
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance is critical to keeping an HVAC system in good condition. Here’s a checklist of key maintenance tasks:
- Change or Clean Air Filters: The air filter should be replaced every 1-3 months, depending on usage. Clean filters help the system run more efficiently and improve indoor air quality.
- Clean Coils and Ductwork: Dust and debris accumulate on both the evaporator and condenser coils over time, which can reduce cooling efficiency. Ductwork should also be cleaned to remove any blockages that may impede airflow.
- Check Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can indicate a leak, which needs to be fixed. Regular checks help maintain optimal cooling performance.
- Inspect and Clean the Condensate Drain: A clogged condensate drain can lead to water damage and mold growth. Ensure it is clear to prevent these issues.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Motors and fans can wear out without proper lubrication, leading to breakdowns. Regular lubrication helps extend their lifespan.
Impact on HVAC purpose: Regular maintenance ensures that the HVAC system continues to provide comfort, energy efficiency, and healthy air quality without sudden breakdowns or inefficiencies.
Signs Your HVAC Needs Repair
There are several warning signs that your HVAC system may need repairs. Catching issues early can help prevent more costly and extensive damage.
Common signs your HVAC system needs repair include:
- Unusual noises: Grinding, rattling, or squealing noises may indicate problems with the fan, motor, or other parts.
- Inconsistent temperature: If some areas of your home or business are too hot or cold despite using the same thermostat, this could signal a problem with airflow or a malfunctioning thermostat.
- Water pooling around the unit: Excess moisture can indicate a clogged condensate drain, refrigerant leak, or other issues.
- Foul odors: A musty or burning smell may suggest mold growth, a burned-out motor, or an issue with wiring.
Impact on HVAC purpose: When HVAC systems start showing signs of malfunction, their ability to maintain consistent temperature control, air quality, and efficiency is compromised.
Hiring an HVAC Professional
When regular maintenance or DIY troubleshooting doesn’t solve the problem, it’s time to call in a professional HVAC technician. A licensed technician can perform in-depth inspections, repairs, and system upgrades.
Things to consider when hiring an HVAC professional:
- Experience: Ensure that the technician is experienced and licensed to work on your specific HVAC system (e.g., central air, heat pump, ductless systems).
- Reputation: Look for reviews, recommendations, and certifications (e.g., NATE certification) to find a reputable professional.
- Preventative maintenance: Many companies offer maintenance packages that include regular inspections and discounts on repairs.
Impact on HVAC purpose: Professional maintenance and repair help restore the system to optimal working condition, ensuring that it serves its purpose efficiently and effectively.

The Future of HVAC: What’s Next for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems?
As technology evolves and concerns about sustainability and energy consumption grow, the purpose of HVAC systems is expanding. HVAC systems are becoming more efficient, smarter, and environmentally friendly.
Innovations in HVAC Technology
The HVAC industry is rapidly adopting new technologies to enhance comfort, energy efficiency, and user control. These innovations not only make systems more efficient but also improve the overall user experience.
- Smart HVAC Systems: Smart thermostats and home automation are now standard in many residential and commercial HVAC systems. These systems can learn user preferences, adjust the temperature based on your routine, and be controlled remotely via smartphone apps. For example, systems can automatically adjust the temperature when no one is home, or cool down the house right before you arrive.Benefits:
- More precise temperature control.
- Increased energy savings.
- Remote monitoring and management via smartphones.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: Geothermal heat pumps take advantage of the constant temperature of the earth’s surface to heat and cool homes. These systems are incredibly energy-efficient and have a long lifespan.Benefits:
- Sustainable energy source.
- Lower operating costs.
- Environmentally friendly with minimal carbon footprint.
- Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems: VRF systems allow for precise control over individual rooms or zones. This technology uses refrigerant as the cooling and heating medium, and it can adjust to the varying needs of each space.Benefits:
- Energy efficiency due to zoned temperature control.
- Reduced energy wastage by cooling or heating only the rooms in use.
- Quiet operation.
- Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) and Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs): These systems exchange heat and moisture between incoming and outgoing air, improving both energy efficiency and indoor air quality by reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.Benefits:
- Improves energy efficiency and reduces heating/cooling loads.
- Better air quality due to enhanced ventilation.
These innovations are making HVAC systems not only more efficient but also more aligned with the needs of modern users, focusing on sustainability and ease of use.
Sustainability Trends in HVAC
As global awareness about climate change increases, the HVAC industry is undergoing a shift toward greener technologies that use less energy, reduce emissions, and minimize environmental impact. Sustainability is becoming a critical focus in both residential and commercial HVAC solutions.
- Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Traditional refrigerants like R-22 have been phased out due to their high global warming potential (GWP). Newer refrigerants, such as R-410A and natural refrigerants like CO2, are gaining popularity. These refrigerants have a much lower environmental impact and help reduce the carbon footprint of HVAC systems.Benefits:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lower environmental impact.
- Compliance with international regulations (e.g., the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol).
- Energy-Efficient Systems: Energy-efficient HVAC systems, certified by Energy Star and other energy ratings, are now common in both residential and commercial buildings. These systems consume less energy to perform the same tasks, reducing operating costs and supporting global sustainability efforts.Benefits:
- Lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
- Fewer carbon emissions.
- Potential for tax credits or rebates for energy-efficient systems.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Some modern HVAC systems are designed to integrate with renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind power. By combining HVAC with renewable energy systems, homes and businesses can achieve a net-zero energy status.Benefits:
- Reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
- Sustainable operation using renewable energy sources.
- Lower overall energy costs.
As sustainability becomes a greater priority, HVAC manufacturers will continue to innovate and develop systems that help meet energy and environmental goals.
The Role of HVAC in Green Building Design
The role of HVAC systems in green building design cannot be understated. Green buildings prioritize energy efficiency, sustainability, and environmental friendliness. HVAC systems play a significant role in achieving the desired outcomes in these types of buildings.
- LEED Certification: The Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification is a globally recognized symbol of sustainability. Buildings that achieve LEED certification often incorporate advanced HVAC systems that meet high standards of energy efficiency and environmental impact.HVAC systems in LEED buildings are often:
- Designed to minimize energy consumption.
- Equipped with energy-efficient components.
- Integrated with renewable energy sources.
- Passive Building Design: In passive homes and buildings, HVAC systems are optimized to work with the building’s natural design to reduce the need for artificial heating or cooling. These homes rely on insulation, natural ventilation, and solar energy, reducing the HVAC system’s overall energy load.Benefits:
- Significant reduction in the need for heating and cooling.
- Lower operating costs.
- Environmentally friendly design.
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): Green buildings often incorporate energy management systems that monitor and control HVAC and other systems to ensure optimal energy performance. These systems allow building owners to track energy usage, identify inefficiencies, and make adjustments as needed to save energy.Benefits:
- Real-time monitoring of energy use.
- Enhanced efficiency through automation.
- Reduced energy waste.
By incorporating cutting-edge HVAC systems and sustainable building practices, green buildings are helping to set the standard for environmental stewardship in the construction industry.
How to Choose the Right HVAC System for Your Home or Business
Choosing the right HVAC system is crucial for ensuring that your needs are met efficiently and cost-effectively. Whether you’re installing a new system or replacing an old one, there are several key factors to consider when selecting an HVAC system.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an HVAC System
The purpose of HVAC systems is to provide comfort, air quality, and energy efficiency. To achieve these goals, it’s important to consider the following factors when choosing an HVAC system:
- Size of the Space: The size of your home or business is one of the most important factors when selecting an HVAC system. If the system is too small, it won’t provide enough heating or cooling. If it’s too large, it will cycle on and off frequently, leading to energy waste and unnecessary wear on the system.Solution: Have a professional HVAC technician perform a load calculation to determine the correct size for your system.
- Climate: Your geographic location plays a big role in deciding whether to invest in a heating or cooling-focused system. If you live in a place with extreme winters, you might prioritize heating capacity. In warmer climates, cooling efficiency will be more important.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for systems with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings. Higher efficiency means lower energy costs.
- Ductwork and Installation: If your home or business already has existing ducts, a central HVAC system might be appropriate. If you don’t have ducts, a ductless mini-split system or heat pump could be a better option.
- Budget: While it’s tempting to choose the cheapest system, remember that the upfront cost is only part of the picture. Consider long-term operating costs, maintenance requirements, and energy savings.
- System Type: Depending on your needs, you might choose between:
- Central HVAC systems (ideal for larger homes and buildings).
- Ductless mini-splits (great for small spaces or homes without ducts).
- Heat pumps (efficient for both heating and cooling).
Consulting with a Professional
When in doubt, always consult with a professional HVAC technician who can help you select the best system based on your specific needs. A professional will consider all of the factors mentioned above and recommend the most suitable HVAC system for your home or business.
The Essential Purpose of HVAC Systems in Modern Life
The purpose of HVAC systems goes beyond just heating, cooling, and ventilation. These systems are critical in maintaining comfort, improving indoor air quality, enhancing energy efficiency, and ensuring healthier living environments. Whether you’re looking to install a new system, maintain an existing one, or upgrade to more energy-efficient options, HVAC systems are essential to modern life.
As technology advances, the role of HVAC systems will continue to evolve, incorporating smarter, more energy-efficient solutions that help meet the needs of homeowners, businesses, and industries. By choosing the right system, scheduling regular maintenance, and staying informed about emerging trends, you can ensure that your HVAC system continues to serve its purpose for years to come.